Google Search Console (GSC) is one of those SEO tools you hear about all the time. Whether you’re a marketer, an SEO beginner, or a business owner trying to understand your website performance. GSC gives you a direct window into how Google actually sees your website.
The best part? It is completely free to use. However, the Google Search Console login can be tricky for a complete beginner. But don’t worry, by the end of this guide, you’ll know exactly how GSC works, so you can use its useful insights & reports to make your website win in 2026.
What is Google Search Console?

Google Search Console (formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools) is a collection of free tools and technical reports that help website owners monitor, maintain, and optimize their website presence. GSC gives detailed visual data of how Google crawls, indexes, and displays a website on its search engine results pages.
The tool gives important performance metrics like clicks, impressions, source of traffic, and many more. This data helps webmasters (the person operating the site) in monitoring their overall website health and generating more traffic/visits.
What Does Google Search Console Do & Why to Use It?
Search Console shows you how Google sees your website. Not how you think it looks. Not what a tool guesses. What Google actually does with it. If you’re doing SEO or running a site, this matters. A lot.
Google Search Console tells you if Google has taken any manual action against your site. That’s basically a penalty, and if it happens, your pages can vanish from search without warning. It also lets you remove pages temporarily when something goes wrong—wrong page indexed, outdated content, or something that shouldn’t be public.
Changing your domain? There’s a tool for that, too. You can officially tell Google your site has migrated.
It also highlights structured data issues, so you know why your pages aren’t showing fancy results like FAQs or reviews.
For technical checks, Search Console helps you see which pages aren’t indexed, inspect individual URLs, catch security problems, and understand how fast (or slow) real users experience your site through Core Web Vitals.
Simple truth: if SEO matters to you, Google Search Console isn’t optional. It’s the one place where Google actually explains what’s happening behind the scenes.
How To Get Started With Google Search Console?
Getting started with Google Search Console login is lengthy but not complicated. You don’t need technical SEO experience. Just follow the steps, and you will be logged in and accessing all the juicy insights of GSC in a few minutes.
Step 1 – Sign in with your Google Account
You can access Search Console through your Google account. If you already use Gmail or Google Analytics, use that. If not, create one just for your website so things don’t get messy later. Once you’re signed in, you’re ready.
Step 2 – Open Google Search Console
Then go to Google Search Console and click “Start Now.”
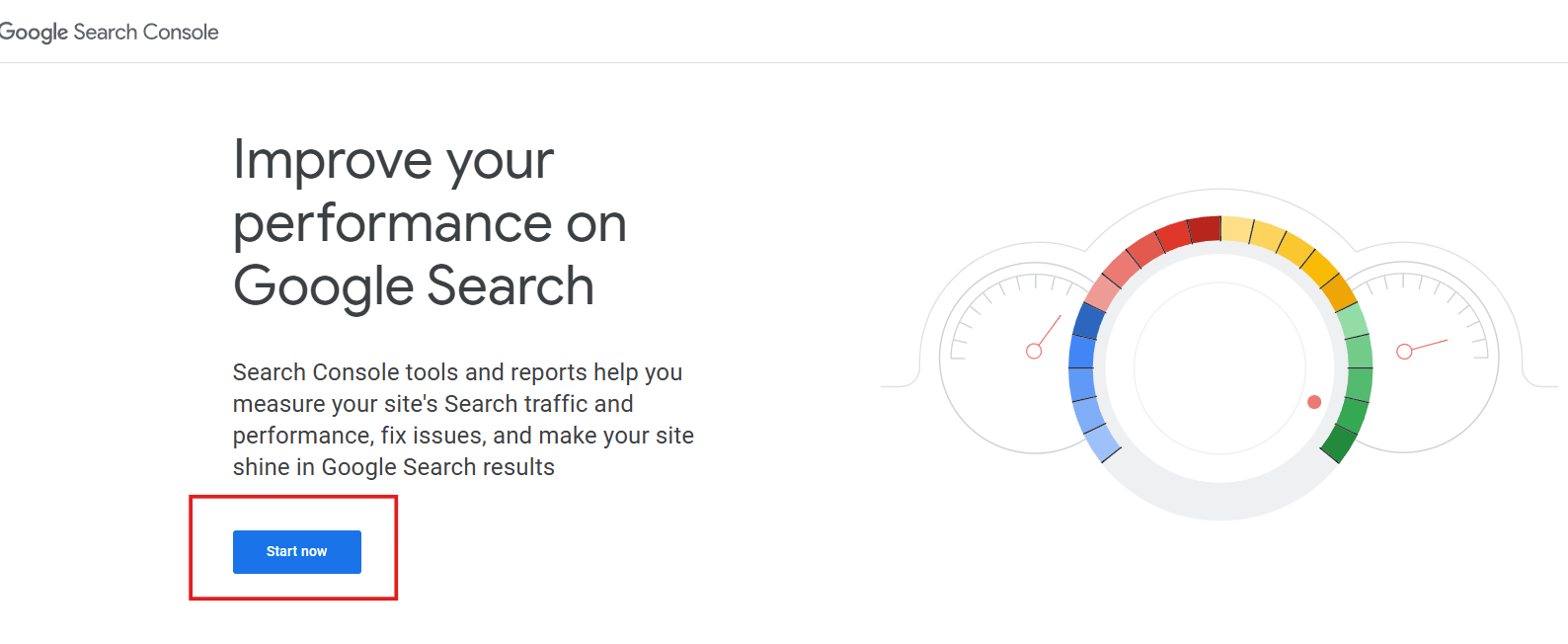
Now, you will see a dashboard asking you to add your domain.
Step 3 – Add Your Website (Domain vs URL Prefix)
There are two ways to add your property or website – Domain and URL Prefix.
If you are choosing to add your website through the domain property option. It is followed by DNS verification. (will discuss this later on). It tracks the entire website, including all of your subdomains and protocols. It is a little lengthy option, but it gives a clear picture.
Meanwhile, if you are going with the URL prefix option. It is a little easier to verify your website, as it tracks only a specific version of your website. (for example, https://www.mysite.com, not blog.mysite.com.) You can easily verify your website by uploading an HTML file, or through Google Analytics or Tag Manager.
If you are still confused about choosing between the two –
- Go for Domain if you want full coverage for each subdomain or protocol and have DNS access.
- Choose URL prefix if you just want to track a specific version of your website.
Step 4 – Verify Ownership
Google Search Console needs to verify that you have access to the website you want to track insights for.
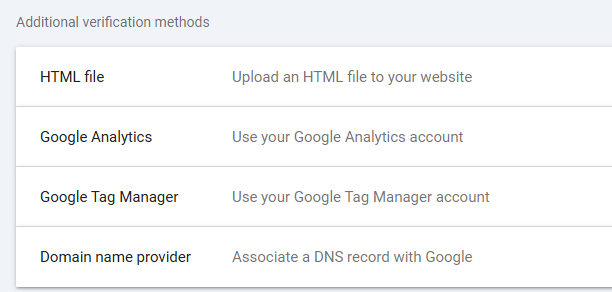
There are several methods you can choose from-
-
DNS Verification
Add the TXT record provided by Google to your domain’s DNS settings (through your domain provider).
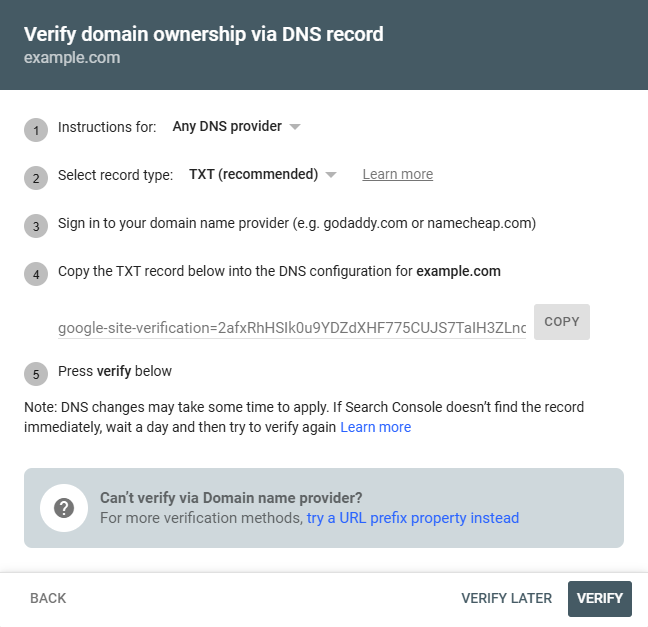
This method takes some time to update, but it is highly reliable.
2. HTML File Upload
You can also complete Google Search Console verification by uploading to your website’s root directory.
Download the verification file from Google and upload it to your site’s root directory. Once uploaded, click “Verify” in the Search Console.
3. HTML Tag
Copy the meta tag Google gives you and place it in the <head> section of your website. Most CMS platforms provide a simple field where you can add this tag.
4. Google Analytics
If GA4 is already installed on your site, you can verify ownership through the same Google account associated with it.
5. Google Tag Manager
If GTM is properly added to your site, verification can be completed instantly using your Tag Manager container.
How to Add a Sitemap in Search Console?
Adding a sitemap in Google Search Console helps Google understand your site structure and crawl your pages more efficiently. Think of your sitemap as a roadmap; it shows search engines every important URL you want indexed.
1. Check if Your Website Already Has an XML Sitemap
Before creating anything new, confirm whether your site already generates a sitemap.xml file.
Try visiting:
- yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
- yourwebsite.com/sitemap_index.xml
If one of these loads is your active XML sitemap.
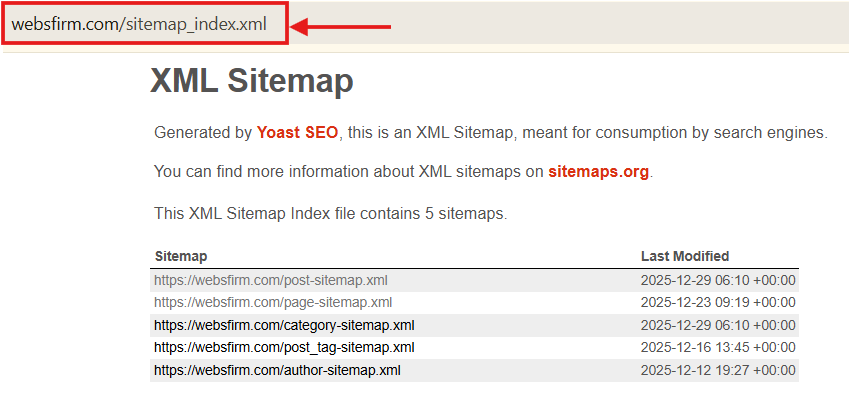
If nothing appears or you get a 404 error, you’ll need to generate one.
2. Create an XML Sitemap (If Needed)
If you are using WordPress, then you can simply use Yoast, RankMath, or AIOSEO plugins to generate your sitemap. These plugins will automatically create & update one. You can also use simple tools like XML-Sitemaps.com to generate a sitemap.
But you must give valid URLs, which shouldn’t redirect, to get a clean sitemap.
3. Submit Your Sitemap in Google Search Console
Now you need to hook it up with the Search Console of Google for better crawling and indexing by the search engine.
- Open the Google Search Console.
- Indexing → Sitemaps From the left sidebar.
- Enter your sitemap URL in the “Add a new sitemap” box.
- Click Submit.
Once you submit, GSC will fetch your sitemap and start processing the URLs inside the sitemap.
4. Check Your Sitemap Status Regularly
After submitting the sitemap, Search Console’s dashboard will show the status. If you see warnings like “indexed, not submitted,” “Crawled, not indexed,” or “Blocked by robots.txt,” then there must be some technical SEO related issue.
In most cases, Google Search Console isn’t managed by just one person. Someone might need access to check performance, someone else to look at technical issues, and sometimes a developer just needs to see what’s going on. You can easily share access to your Google Search Console without sharing your Google login.
There are two kinds of roles/access you can give-
- Owner – With this access, anyone can get full access to your GSC account. They can manage users, setting and verifications.
- User – This option is ideal for anyone who wants to view reports and data, but doesn’t want to affect the property.
For most situations, user access is enough. To add someone, open Google Search Console and choose the property. Go into Settings, then open Users and permissions. Add the email address and select the role. That’s it.
How to Connect Google Search Console With Google Analytics (GA4)
Search Console shows how your site appears in Google search results. While GA4 focuses on how user behaves when using your website. After linking both tools, you can see the full story.
You are no longer guessing if traffic from Google is working. You can actually check what the visitors are doing. Are they reading the things you wrote? Are they clicking on things?. Are they leaving your website right away? Traffic, from Google, is something you want to know about.
Steps to Connect Google Search Console with GA4
- Open Google Analytics.
- Click Admin in the bottom-left corner.
- Under Product links, select Search Console Links.
- Click Create link and choose your verified Search Console property.
To finish the setup, you need to have owner access in both tools. This means you have to be the owner of both tools to complete the setup. The owner’s access is necessary for both tools.
Where to View Search Console Data in GA4?
Go to Reports → Acquisition → Search Console.
To find out what people looked for, you can use the Search queries report. This report shows you what users searched for. You can use these reports to get information about the search terms people are using to reach your website. Furthermore, you could also use landing page reports to get insights to find out which pages people visited from Google.
This is a way to see what people are looking at when they come to your site from Google. You can use the Landing pages report to get this information. These reports combine search data with user actions, making analysis easier and more useful.
Understanding GSC Metrics
Before getting to know how Google Search Console works. It is important to know about the main metrics. As you are going to see lots of these after login. Let’s get an overview of basic metrics.
Queries
Queries are the words and phrases people type into Google that lead them to your site. Looking at queries helps you understand what your audience really wants.
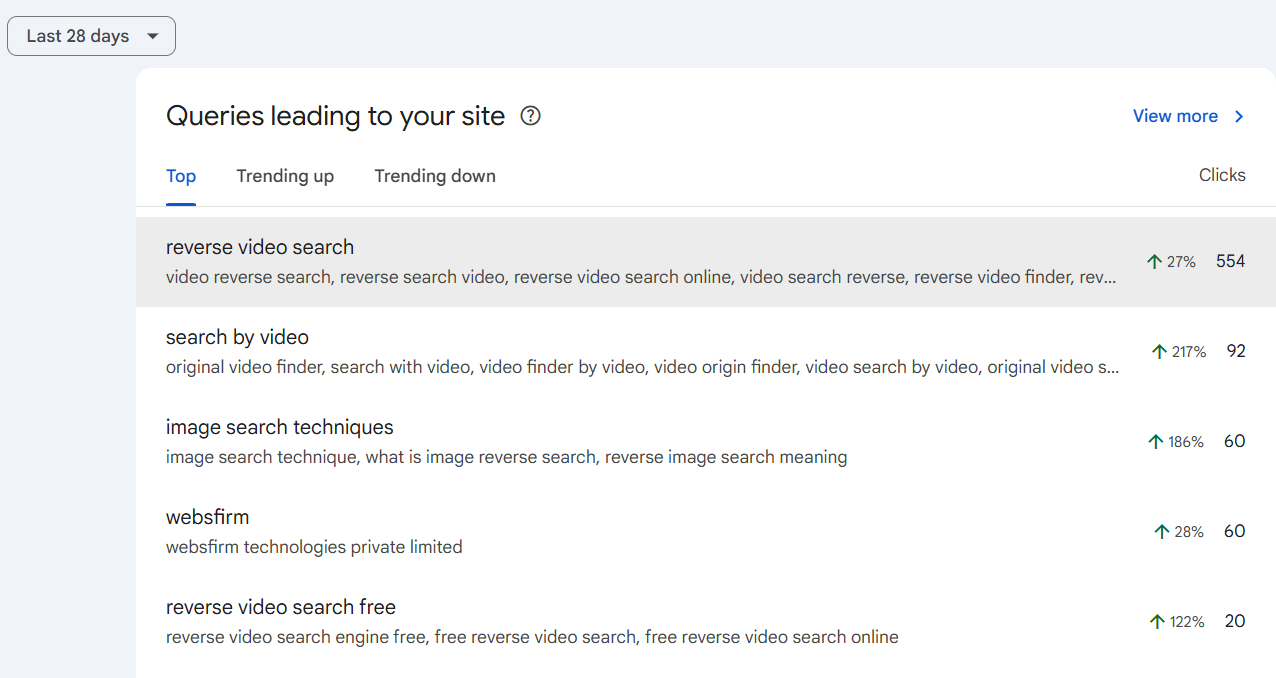
You can see which keywords are driving traffic, find gaps where you could create new content, and make sure your pages answer the questions users are actually asking.
Pages
“Pages” allows you to see the URLs that are getting click traffic from the searches. This is your reality check because, in essence, this allows you to see the click traffic from the search on the pages.
There are sure to be pages where you are surprised, good or bad. And then there are sure to be some where help is needed. This report, over time, assists you in determining where your attention needs to focus versus simply choosing entries at random because it doesn’t matter anyhow.
Impressions
Impressions are the number of times that your page appears in the search results on Google. It’s not the number of times it’s been clicked on; it’s the number of times it appeared in the search result page.
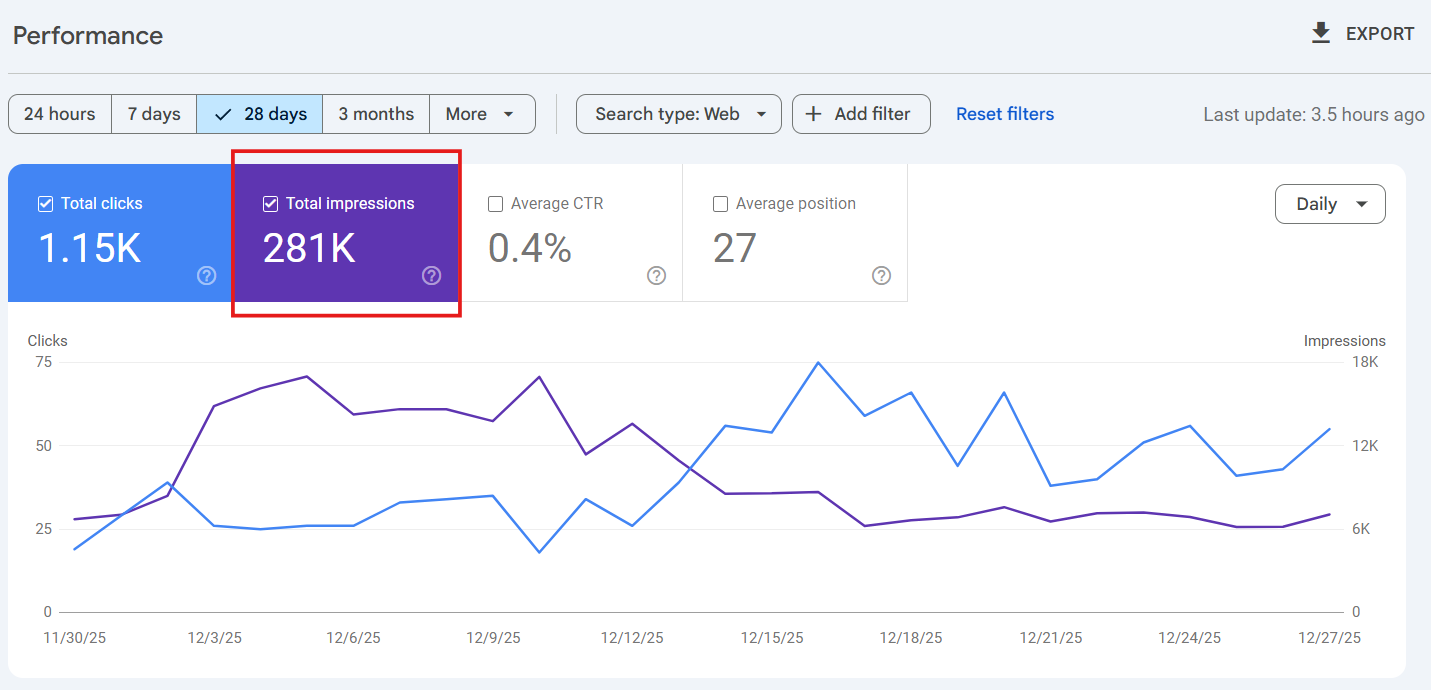
If your impressions are strong, but your clicks are poor, it’s obvious that something is not clicking (oh, the irony!). More often than not, this is related to your title, description, and /or a mismatch between intention and what you’re actually delivering on the landing page. I would use impressions to see where you’re at before trying to address traffic issues.
Clicks
It shows the number of clicks on your site by the number of Google site visitors. This seems to be more apt than the word ‘impressions.’ Clicks refer to the number of clicks on.
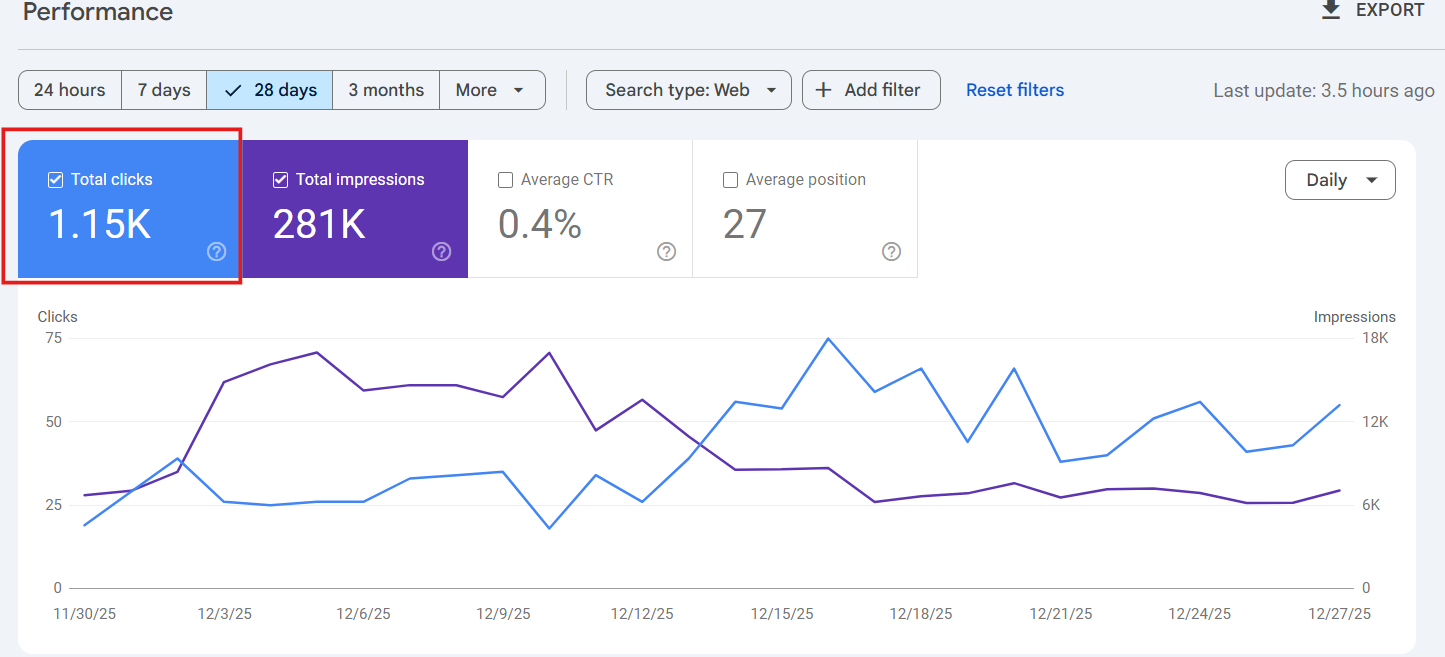
Sometimes, an easy win comes from a page with a low click-through rate and a large impression rate. You won’t have to rewrite the article, and it may be enough to optimize its appearance on the engine simply. Small changes sometimes provide an edge.
Average Position
“Average position” will tell you more or less where your page is positioned within the search result listing.
The metric has some flaws, but it can still be considered helpful.
“If your position is changing for the better over time, then changes to your Search Engine Optimization are definitely happening. But if your position is changing for the worse, then a fix is in order. While not an analytical metric on its own, together with Impressions and Clicks, it is a valuable tool.”
Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
Click-Through Rate ( acronym for “click through rate”) represents the rate of people who actually click on a page viewed. One of the reasons why there may be a low CTR may lie in the way the page is displayed and may have nothing to do with the Google page rank you receive.
Google’s Search Console offers you the ability to spot pages where more views can be achieved through optimized titles and descriptions without actually editing the content on the page. There are no easier modifications that you may want to attempt.
How to Use Google Search Console (Step-by-Step)
Google Search Console (GSC) is your free dashboard for tracking how Google sees your website.
Whether you’re new to it or brushing up, this step-by-step walks you through the essentials. Let’s dive in.
-
Check Indexing Status
“Indexing” means Google adding your pages to search results. This report tells you which pages made the cut.
How to check which pages are indexed?
- Click “Pages” on the left sidebar (it’s under “Indexing”).
- You’ll see a simple dashboard: total pages Google knows about, how many are indexed, and why others aren’t.
- Click “View details” to see the list.
- Download the list as a spreadsheet to have a clear picture.
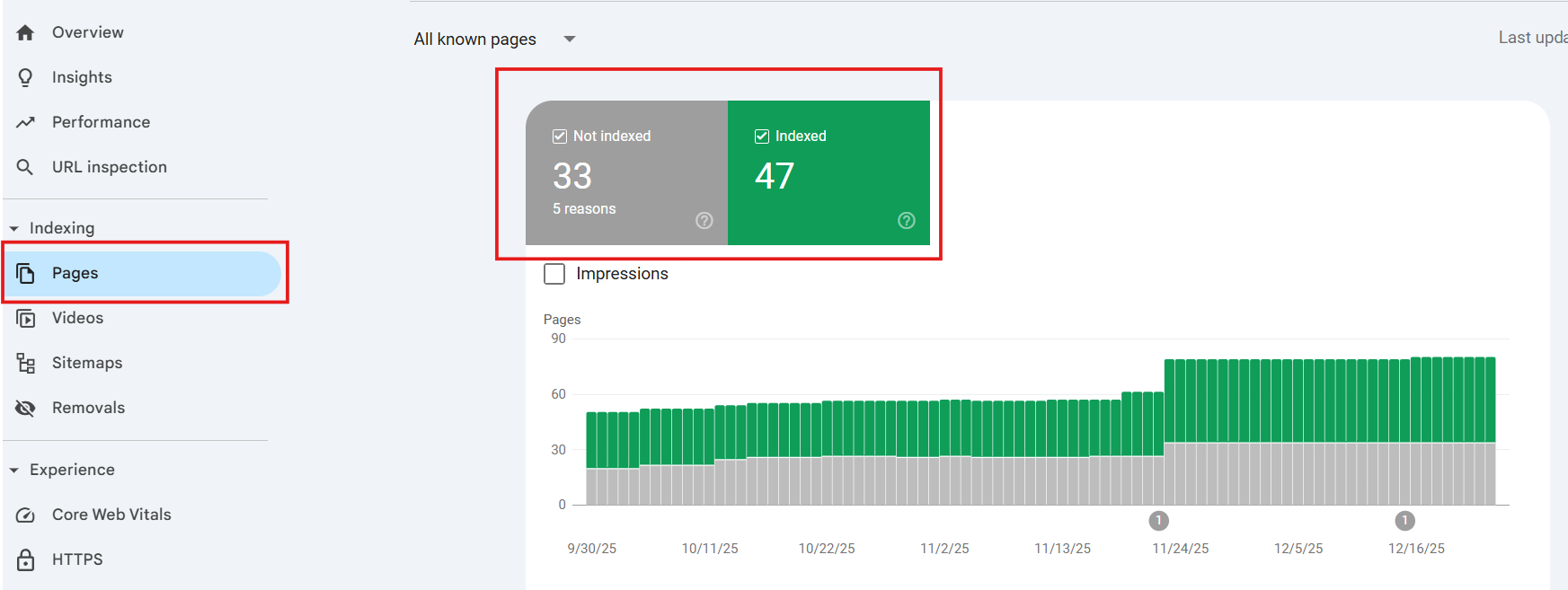
How to fix indexing errors?
Next, identify specific errors like “Blocked by robots.txt” or “Server error (5xx).” For robots.txt blocks, edit the file to allow crawling, save changes, and monitor progress; for duplicates, implement canonical tags.
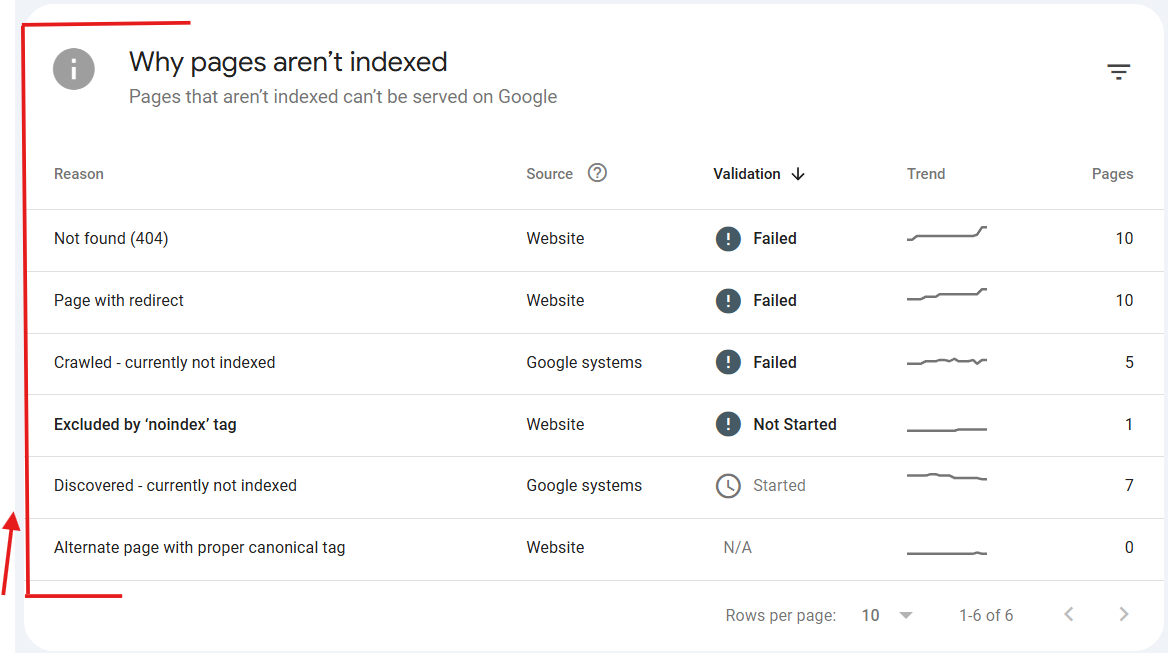
After fixes, Google often resolves these automatically within a few days, but you can speed things up with the URL Inspection tool covered next.
-
Use the URL Inspection Tool
URL inspection is a go-to tool for troubleshooting or getting a complete diagnostic of each URL, mainly for indexing purposes.
You can easily access it directly from the search bar of the Google Search Console dashboard.
How to Request Indexing in Google Search Console?
There are two ways to use the URL Inspection tool:
- Type the full URL you want to check in the search bar at the top of any Search Console page. Make sure the URL is for the property you are currently viewing.
- Click the Inspect link next to a page URL in most reports. You might need to hover over the URL to see this option.
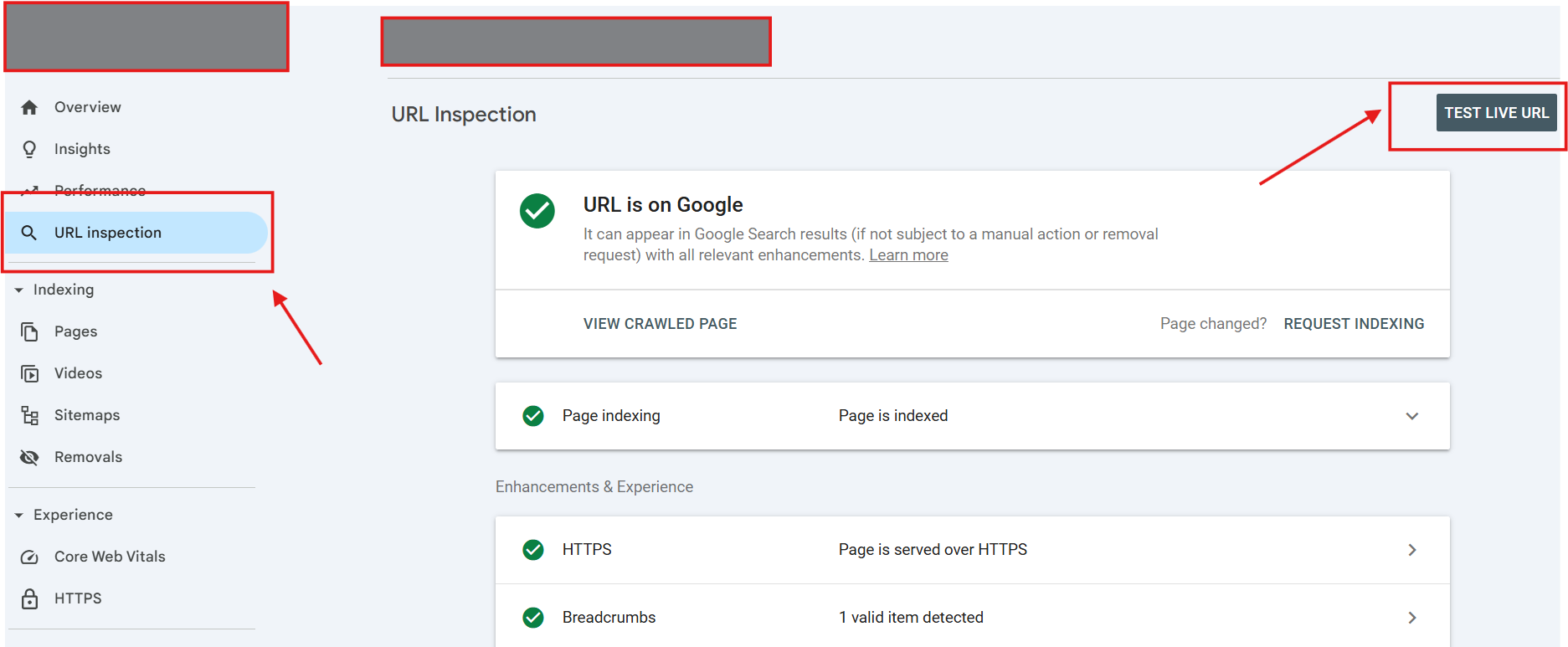
Select “Test Live URL” to check an instant report of any URL’s indexing status, mobile usability, or any potential errors.
-
Monitoring Performance Report
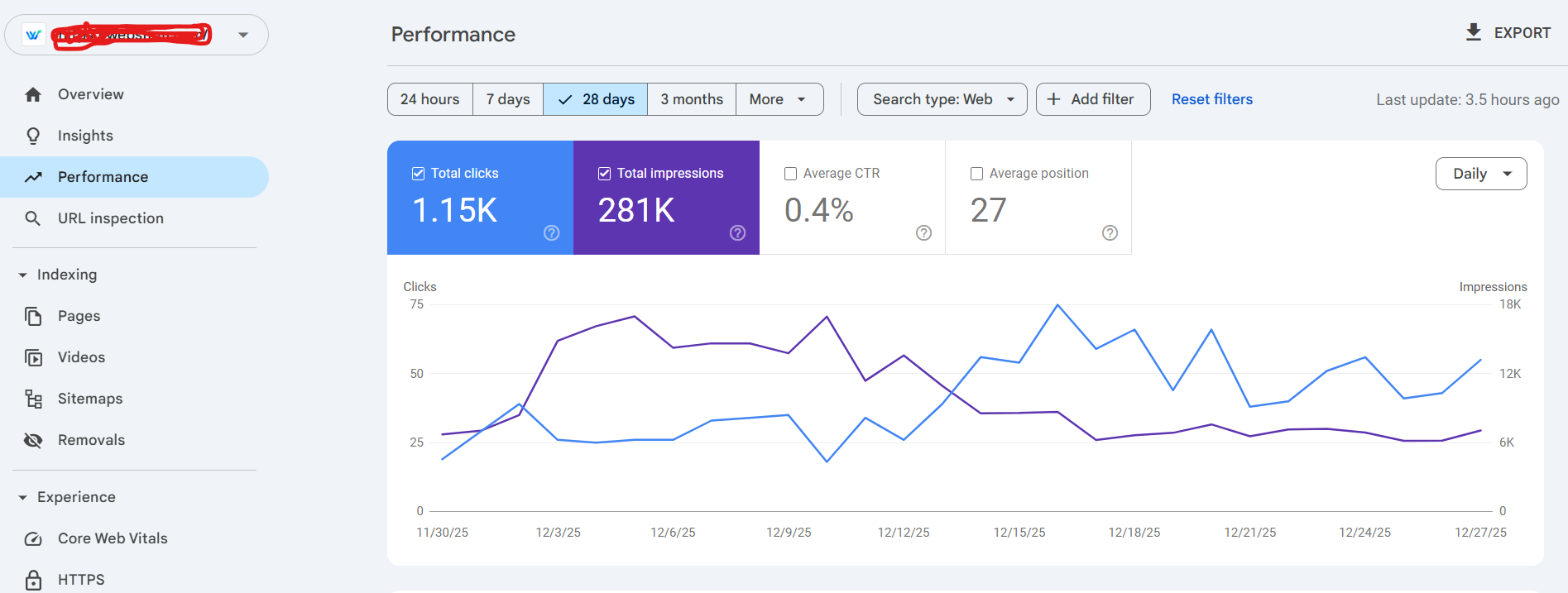
Once indexing is done, let’s explore the “Performance” report in GSC.
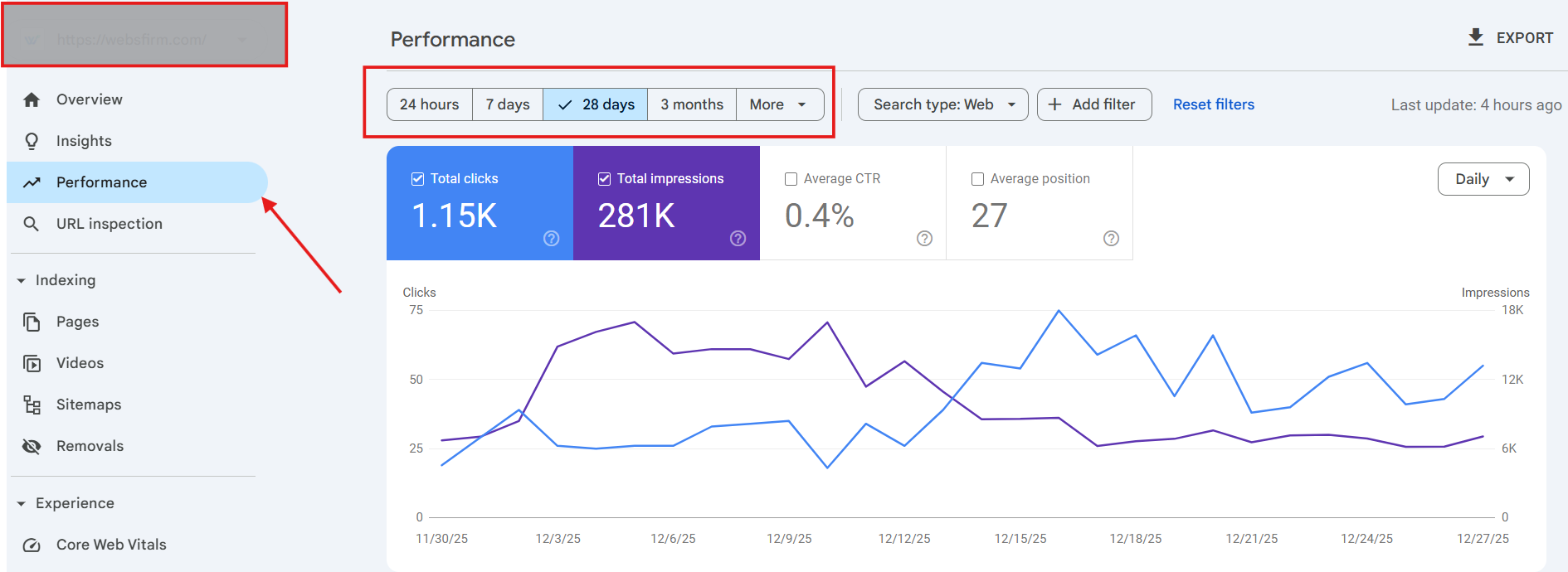
This report gives insights into traffic, clicks, total impressions, and ranking. You can select/ customize dates as per your needs,
How to find top traffic pages?
Switch to the “Pages” tab and sort by “Clicks” in descending order to spotlight your highest performers.
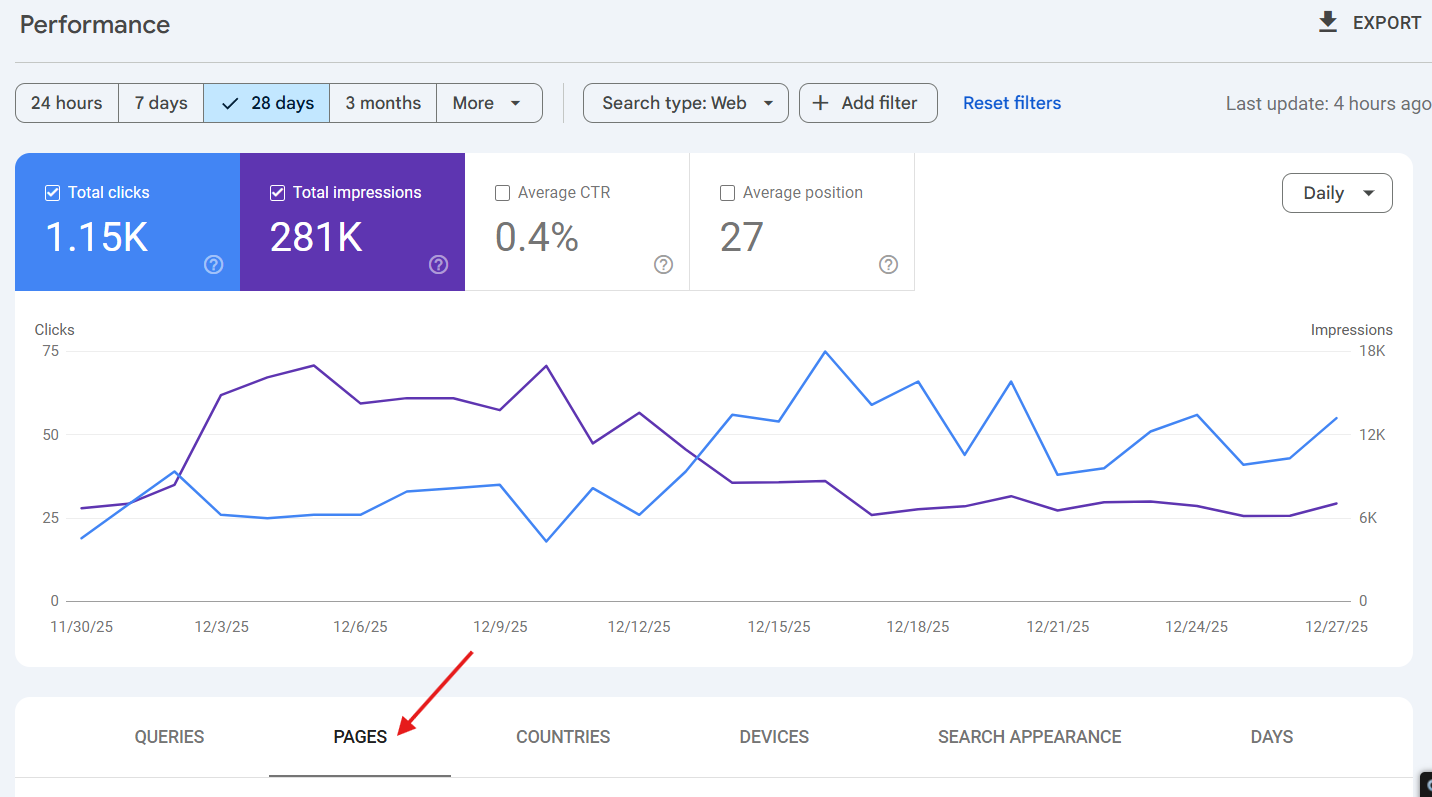
Optimize these pages to gain more traffic.
How to find the best-performing keywords?
Go to the “Queries” tab, sort by clicks, and note high-impression, low-click terms; optimize titles and content to boost click-through rates.
How to find pages stuck on page 2?
Apply filters for pages with deep impressions (over 1,000) but low clicks and positions beyond 10,these need lifts like better internal linking or content refreshes.
How to compare performance by device & country?
Add dimensions via the filter icon, such as “Device” or “Country,” to uncover trends like mobile underperformance, guiding targeted improvements.
-
Checking Mobile Usability
With mobile-first indexing in effect, the Mobile Usability report, located under “Experience,” becomes crucial, as it highlights phone-specific hurdles with visual aids. Transition to the next performance to ensure broad accessibility.
How to read mobile issues?
Scan for errors like “Text too small to read” or “Clickable elements too close together,” then click affected URLs for screenshots that make problems crystal clear.
-
Check Page Experience & Core Web Vitals
Staying in “Experience,” Core Web Vitals in the GSC tool gauge real-user interactions with three metrics (green if 75%+ pass), important for rankings.
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): Main content paints in under 2.5 seconds? Compress hero images and ditch render-blocking JS to speed it up.
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): No annoying jumps under 0.1? Reserve space for images and ads upfront.
- INP (Interaction to Next Paint): Clicks respond snappily under 200ms (the fresh 2024 replacement for FID)? Trim heavy scripts and third parties.
How to use this data to fix things?
Filter “Poor” URLs, feed them into PageSpeed Insights for step-by-step fixes like lazy-loading, roll out site-wide, and track the green-up in your Search Console dashboard weekly.
-
Using the Links Report
The Links report in Google Search Console (GSC) shows how other sites link to yours and how your pages connect internally, key to better rankings. Just click “Links” in the left sidebar to dive in.
How to Use Google Search Console to Improve SEO?
Google Search Console shows exactly how your website is performing in search results.
There are several data points you can use to improve rankings, traffic, or even catch any SEO issues before they even occur.
Improve Rankings for Pages You Already Have
You don’t always need new content. Many pages are already close to ranking better.
In the Performance report, you can find pages that get impressions but are not yet at the top. These pages already have Google’s trust. Small changes like clearer content, better matching search intent, and internal links can help them rank higher without writing anything new.
This is one of the easiest ways to see quick results.
Find Useful Keywords In Google Search Console
Search Console shows real search terms people use to find your site. In the Queries report, you may notice keywords your content mentions, but it does not fully explain. These terms or search queries can help you in improving your current or create new ones for blogs or landing pages. Since Google already shows your site for these terms, it is easier to rank for them compared to random keywords. This helps your website grow organically.
Get More Clicks from the Same Rankings
Sometimes pages appear in search results, but people don’t click.
The GSC tool shows which pages have many impressions but few clicks. In most cases, the title or description is the problem. Making them clearer and more helpful can bring more traffic, even if your ranking stays the same.
This is a simple fix that many people miss.
Fix Pages Before Traffic Drops
Traffic usually drops slowly, not all at once.
By checking past and present data, you can see when a page starts losing clicks or impressions. This helps you understand if the content is outdated or no longer matches what people want. Updating pages at the right time helps protect your rankings.
SEO is not only about growing. It is also about keeping what already works.
Common Errors in Google Search Console + How to Fix Them
-
Crawled, Currently Not Indexed
This status means Google has crawled the page but has chosen not to index it. In most cases, this decision is about content quality rather than a technical issue. Pages with thin content, duplicated information, or weak internal links often fall into this group.
To fix this, focus on improving the page itself. Strengthen the content, add internal links from relevant pages, and ensure the page has a clear purpose. After making changes, use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to request indexing again.
-
Discovered, Currently Not Indexed
Here, Google knows the page exists but has not crawled it yet. This usually happens with new pages, large websites, or sites with limited crawl signals. Poor internal linking or sitemap issues can also slow down crawling.
Make sure the page is included in your XML sitemap and is linked from important sections of your site. Over time, Google will crawl the page once it detects stronger signals that the content is worth indexing.
3. Soft 404 Errors
A soft 404 occurs when a page resembles an error page but still returns a success status code. Google sees these pages as low-value because they don’t provide meaningful content, even though they load correctly.
If the page should not exist, return a proper 404 or 410 status. If the page is valid, add useful content so it clearly serves a purpose. Google Search Console will automatically re-evaluate the page after detecting changes.
4. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content issues arise when multiple URLs display the same or nearly identical content. This makes it hard for Google to determine which version should rank. As a result, none of them may perform well.
Using canonical tags, consistent URL structures, and proper redirects helps resolve this issue. The URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console can confirm which version Google sees as the primary page.
5. Redirect Issues
Redirect problems happen when Google cannot follow a redirect properly. This includes redirect loops, long redirect chains, or redirects pointing to non-indexable pages.
Fix these by keeping redirects simple and direct. Ensure the final destination loads correctly and returns a valid status code. After correcting the issue, revalidate it in Google Search Console to confirm the fix.
Summary
Google Search Console is essential for understanding how Google crawls, indexes, and ranks your website. It connects technical health, content performance, and user behavior in one place.
When used consistently, Google Search Console helps improve existing rankings, uncover keyword opportunities, increase clicks, and respond quickly to performance changes. For long-term SEO success, it should be part of every optimization workflow, not an afterthought.

Experienced Digital Marketing Specialist with a passion for driving online visibility and growth. I am dedicated to driving digital success through effective SEO, SMO, PPC, link building, and Guest Posting outreach strategies. I am eager to leverage my skills and experience to help businesses thrive in the competitive online landscape. I’m Post Graduate with M.Sc. Statistics, and I holds a strong academic background in Mathematics and Statistics, with expertise in Big Data, Data Analysis, and Data Science, creating insightful, data-driven content for modern readers.